41 pricing zero coupon bonds
Zero Coupon Bond - Explained - The Business Professor, LLC Calculating the Price of a Bond. Below is the formula for calculating the present value of a zero coupon bond: Price = M / (1 + r)^n where M = the date of maturity r = Interest Rate n = # of Years until Maturity If an investor wishes to make a 4% return on a bond with $10,000 par value due to mature in 2 years, he will be willing to pay ... Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond (also discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. Unlike regular bonds, it does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero-coupon bond.When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par (or face) value. Examples of zero-coupon bonds include US Treasury bills, US ...
probability - Pricing a Zero-Coupon Bond - Mathematics Stack Exchange There are avaiable 4 zero-coupon bonds, for which maturity date are t = 1,2,3 and 4 respectively; At the moment t=1 will appear one out of three possible states of the market: $\omega_1$, $\omega_2$ or $\omega_1$. There is no possible transaction between the moments 0 and 1, and the prices of bonds in above states are as follows:
Pricing zero coupon bonds
What does it mean if a bond has a zero coupon rate? - Investopedia For example, a $1,000 bond issued with a 4% coupon rate pays $40 in interest annually regardless of the current market price of the bond. If interest rates go up to 6%, newly issued bonds with a ... Zero Coupon Bond Calculator - What is the Market Price? - DQYDJ The zero coupon bond price formula is: \frac{P}{(1+r)^t} where: P: The par or face value of the zero coupon bond; r: The interest rate of the bond; t: The time to maturity of the bond; Zero Coupon Bond Pricing Example. Let's walk through an example zero coupon bond pricing calculation for the default inputs in the tool. Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Unique Advantages of Zero-Coupon U.S. Treasury Bonds. Treasury zeros zoom up in price when the Federal Reserve cuts rates, which helps them to protect stock holdings at precisely the right time ...
Pricing zero coupon bonds. What are Zero-Coupon Bonds? (Definition, Formula, Example, Advantages ... Calculating the price of zero-coupon bonds varies depending on whether the bonds offer annual or semi-annual compounding. The calculation of the price of a bond is given in two illustrations below: Annual Compounding Bonds; Mr. Tee is looking to purchase a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $50 and 5 years till maturity. The interest rate on ... Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula Therefore, a zero-coupon bond must trade at a discount because the issuer must offer a return to the investor for purchasing the bond. Pricing Zero-Coupon Bonds. To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond, use the following formula: Where: Face value is the future value (maturity value) of the bond; r is the required rate of return or ... Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Because zero coupon bonds pay no interest until maturity, their prices fluctuate more than other types of bonds in the secondary market. In addition, although no payments are made on zero coupon bonds until they mature, investors may still have to pay federal, state, and local income tax on the imputed or "phantom" interest that accrues each year. How Premium Bonds are Priced | Zero Coupon Bond | Savings - PFhub Pricing a Zero Coupon Bond. A zero coupon bond does not make any interest payments throughout the life of the bond. There is only a single cash flow, at the time of maturity of the bond, when the par value of the bond is returned to the investors. Pricing such a bond is much simpler. Let's consider a zero coupon bond with a par value of ...
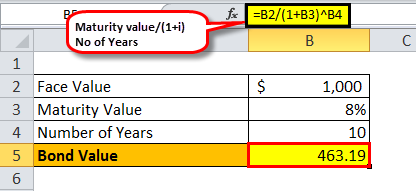
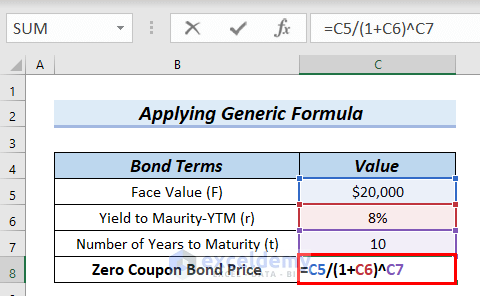
Zero Coupon Bond - (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) = $463.19. Thus, the Present Value of Zero Coupon Bond with a Yield to maturity of 8% and maturing in 10 years is $463.19. The difference between the current price of the bond, i.e., $463.19, and its Face Value, i.e., $1000, is the amount of compound interest Compound Interest Compound interest is the interest charged on the sum of the principal amount and the total interest amassed on it so far. Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Calculator [Excel Template] Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula. To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond - i.e. the present value (PV) - the first step is to find the bond's future value (FV), which is most often $1,000. The next step is to add the yield-to-maturity (YTM) to one and then raise it to the power of the number of compounding periods. The Cash Account and Pricing Zero-Coupon Bonds - Coursera In this module, we're going to discuss the cash account and pricing zero-coupon bonds in the context of the binomial model for the short rate. The cash account and zero-coupon bonds are extremely important securities and derivatives pricing in general and so we're going to spend some time now figuring out how to price them and understand the ... Zero coupon Bonds — Quicken September 1. For background, zero coupon bonds are purchased at steep discount to face value. Interest is earned on the bond and is paid at maturity when the bond is reddened at face value. To record this in quicken requires 3 transactions; 1) An Interest Income transaction - for the amount of interest, 2) A negative Return Of Capital ...
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia Zero-Coupon Bond: A zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full ... The Zero Coupon Bond: Pricing and Charactertistics This means if we pay something around $72 (100-28) on December 1, 1996 for the $100 coupon due on December 1, 2001, we will earn something around 30% over the period or 6% a year. Pulling out our trusty bond calculator, we can actually do the calculation. At a semi-annual yield of 5.6%, the price works out to be $75.91. How to Calculate Yield to Maturity of a Zero-Coupon Bond Consider a $1,000 zero-coupon bond that has two years until maturity. The bond is currently valued at $925, the price at which it could be purchased today. The formula would look as follows ... What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Characteristics & Example Zero-Coupon Bond Pricing Example If an investor wanted to make 5% imputed interest on a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $15,000 that matures in four years, how much would they be willing to pay?
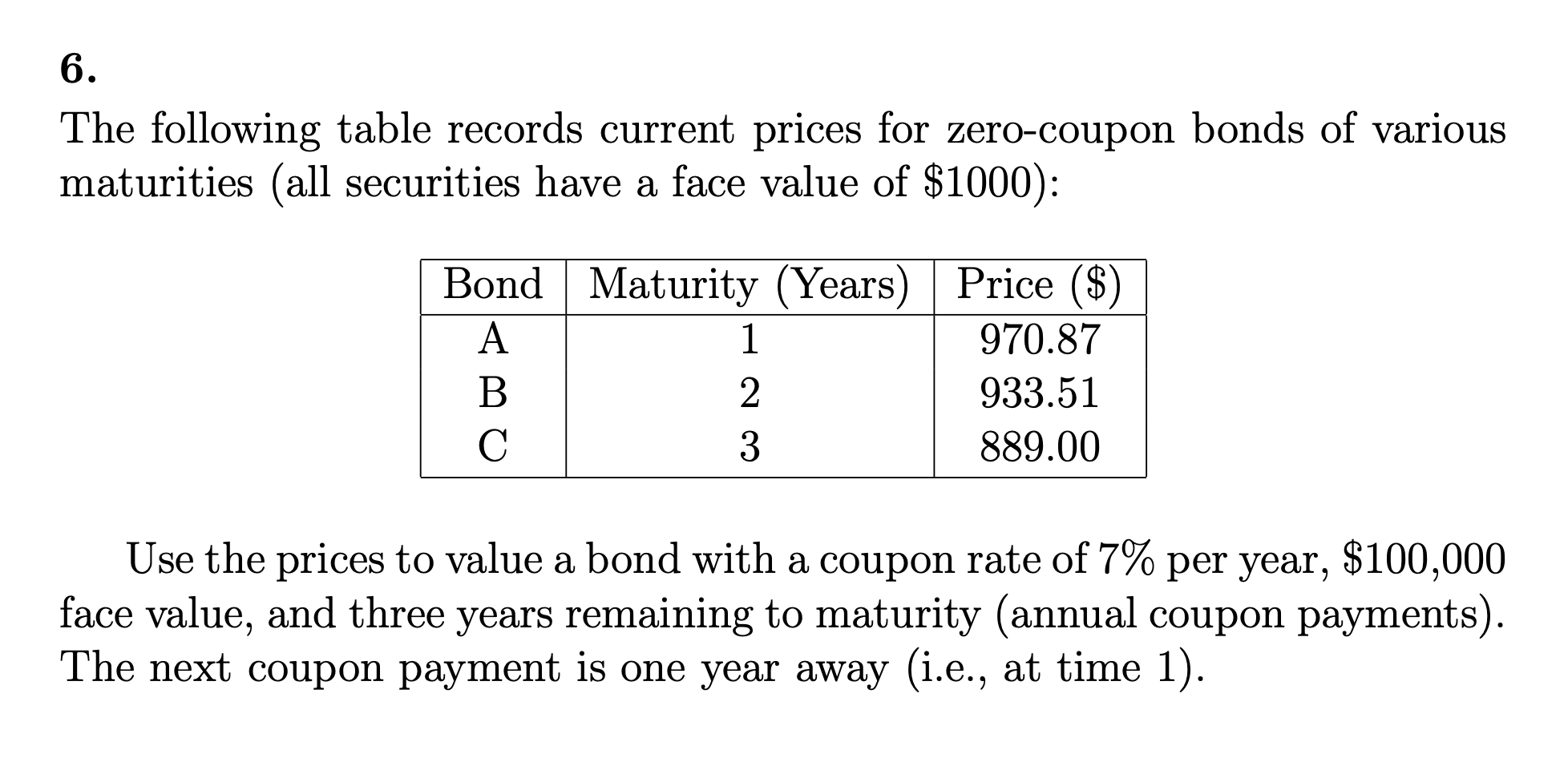
How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price - Double Entry Bookkeeping The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816) The present value of the cash flow from the bond is 816, this is what the investor should be prepared to pay ...
Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to Maturity ... Calculate Zero-coupon Bond Purchase Price. Home / Savings / Calculate Purchase Price of Accrual Bonds / ... And it's been a tremendous asset, as a matter of fact, since the early '80s, and we have documented that these zero coupon bonds have outperformed the S&P 500 by five times- that's including dividends in the S&P, but a lot of people, they ...
Zero-Coupon Bonds and Taxes - Investopedia Zero-coupon bonds are more volatile than coupon bonds, so speculators can use them to profit more from anticipated short-term price movements. Zero-coupon bonds can help investors to avoid gift ...
Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Unique Advantages of Zero-Coupon U.S. Treasury Bonds. Treasury zeros zoom up in price when the Federal Reserve cuts rates, which helps them to protect stock holdings at precisely the right time ...
Zero Coupon Bond Calculator - What is the Market Price? - DQYDJ The zero coupon bond price formula is: \frac{P}{(1+r)^t} where: P: The par or face value of the zero coupon bond; r: The interest rate of the bond; t: The time to maturity of the bond; Zero Coupon Bond Pricing Example. Let's walk through an example zero coupon bond pricing calculation for the default inputs in the tool.
What does it mean if a bond has a zero coupon rate? - Investopedia For example, a $1,000 bond issued with a 4% coupon rate pays $40 in interest annually regardless of the current market price of the bond. If interest rates go up to 6%, newly issued bonds with a ...

![Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Calculator [Excel Template]](https://wsp-blog-images.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2022/01/28183250/Zero-Coupon-Bonds-Formula.jpg)

























Post a Comment for "41 pricing zero coupon bonds"